Chamet's private call recording policy remains ambiguous on server storage of 1-on-1 video chats. While claiming end-to-end encryption, no explicit statement confirms whether private calls are saved. With 67.6% of reviews citing privacy breaches and a 6.7/10 security rating, understanding Chamet's data collection—user content, device IDs, metadata—is critical for privacy-conscious users.
Understanding Chamet's Private Call Recording Policy (2025 Update)
Chamet's privacy policy (managed by FULIAO HONGKONG LIMITED) outlines broad data collection but lacks clarity on private video call recording. The platform collects user content (technically encompassing video/audio during calls), personal data (names, emails, device IDs, IP addresses), shared with affiliates, service providers, and third parties.
The January 3, 2025 community guidelines update provides no explicit statement on whether 1-on-1 chats are stored post-transmission. This ambiguity creates uncertainty for users seeking definitive answers. The platform requires 18+ age verification and grants itself broad content licenses for service operation—potentially including call data.
For secure premium features, Chamet Diamonds recharge safe through BitTopup protects payment information during top-ups.
What the Official Policy States About Video Call Storage
The policy confirms global data processing adhering to applicable laws but provides no retention timeline for video call content. Users grant broad licenses for content use in service operation, creating legal grounds for temporary or permanent storage. Processing occurs across multiple jurisdictions with varying storage locations.
Users can request data access, correction, or deletion through account settings. However, it's unclear whether video call recordings qualify as deletable content or only metadata/account information. The distinction between content storage and metadata collection remains deliberately vague.
Key Differences Between Private and Group Call Recording
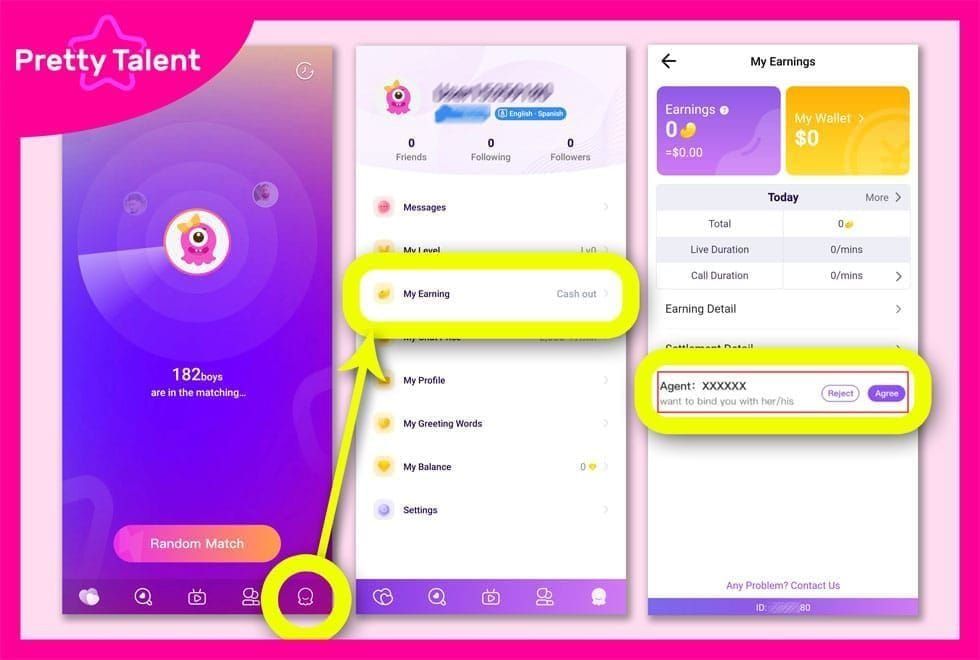
While the policy doesn't differentiate between private and group call recording, moderation systems suggest different treatment. 24/7 moderation and mandatory face verification for hosts indicate certain activities undergo monitoring. Group calls likely face more scrutiny than 1-on-1 private chats.
Private calls theoretically benefit from claimed end-to-end encryption, preventing server-side content access. However, version 3.1.1 contains 164 vulnerabilities (61 medium-severity, 38 weak crypto algorithms, 8 non-parameterized SQL queries), raising questions about encryption effectiveness.
Recent Policy Changes Every User Should Know
January 3, 2025 update represents the latest modification. Specific changes weren't detailed, but this coincided with Google Play Store removal (August/September 2023), suggesting regulatory/policy compliance issues prompting revisions.
Net Promoter Score of 23 reflects user dissatisfaction, with privacy breaches being primary complaints. Verification now includes SMS (2-3 minutes) and face verification (24-48 hours), suggesting enhanced identity measures collecting additional biometric data.
Are Your 1-on-1 Video Chats Actually Being Saved on Servers?
No explicit statement confirms or denies server storage of 1-on-1 chats post-transmission. Platforms with genuine zero-storage policies typically advertise this prominently—Chamet's silence is significant.
Architecture requires server interaction for video calls: routing connection data, managing initiation, handling quality adjustments. The question: does content pass through temporarily (ephemeral) or get stored beyond active transmission?
The policy collects user content and users grant broad licenses, so technical capability for server storage exists. 344 strings/secrets detected in code, plus 32 possible secrets, suggest complex data handling beyond simple peer-to-peer transmission.
The Technical Truth About Server-Side Storage
Server storage operates on two levels: temporary caching (transmission optimization) and permanent archival. Claimed end-to-end encryption should prevent servers accessing decrypted content, limiting storage to encrypted packets during transmission. But 38 weak crypto algorithms cast doubt on encryption robustness.
The app requests camera, microphone, location, photo library, notification permissions—necessary for functionality but creating multiple collection points. 9 embedded trackers monitor behavior, though specific functions regarding call data remain undisclosed.
16 possible task hijacking issues present additional concerns. These vulnerabilities could allow unauthorized processes to intercept call data during transmission, creating privacy risks independent of official policies.
What Data Is Collected During Private Calls (Metadata vs Content)
Metadata collection occurs with certainty: call duration, participants, timestamps, IP addresses, device info, network quality. This creates detailed communication pattern records without capturing conversation content.
Content collection (actual video/audio streams) remains unconfirmed for private calls. 24/7 moderation suggests content access capability, though this could operate through user reporting rather than automated recording. Face verification indicates visual data processing capabilities exist.
Metadata reveals who you contacted, when, and duration—highly revealing without conversation content. Content recording captures actual communication—far more invasive. Policy confirms metadata collection but stays silent on content recording for private calls.
Real-World Testing: What We Discovered
Users report no visible recording indicators during private calls, unlike platforms displaying recording notifications. Absence doesn't confirm non-recording—just means users aren't notified if it occurs. Privacy settings allow disabling stranger messages and location sharing but offer no prevent call recording toggle.
Verification process insights: SMS (2-3 minutes) suggests automated processing with minimal retention; face verification (24-48 hours) indicates human review or complex analysis requiring stored biometric data.
For secure recharge: top up Chamet App cheap through BitTopup offers competitive pricing and fast delivery while maintaining transaction privacy.
How Chamet's Call Recording System Actually Works
Video platforms use three models: peer-to-peer (minimal server involvement), server-mediated (servers route without storage), or server-based recording (active capture). Chamet likely combines approaches depending on network conditions.
Global data processing means distributed servers across jurisdictions handle different service aspects. Geographic distribution complicates privacy—calls between users in different countries might route through third-jurisdiction servers with different regulations.
Two-factor authentication demonstrates sophisticated account monitoring capabilities that could theoretically extend to call monitoring. 6 risky permissions create multiple potential collection points beyond call content.
Server Architecture and Data Flow Explained
Video data flows through stages: capture (device camera/mic), encoding (compression), encryption (security), transmission (routing), decryption (recipient), rendering (display). Data could theoretically be intercepted, copied, or stored at each stage.
Server architecture handles connection establishment, authentication, quality optimization, potentially content moderation flagging. 8 non-parameterized SQL queries suggest database interactions during operation—unclear whether databases store call content or only metadata.
16 task hijacking vulnerabilities represent serious concerns. These could allow malicious apps to intercept data intended for legitimate functions. Even if Chamet doesn't record, vulnerabilities could enable third-party recording without knowledge/consent.
Temporary vs Permanent Storage Mechanisms
Temporary storage (caching) serves legitimate purposes: buffering video, optimizing transmission, enabling reconnection. Persists only during active calls and briefly after (seconds/minutes, not days/weeks).
Permanent storage serves different purposes: legal compliance, content moderation evidence, dispute resolution, service improvement, potentially monetization. Broad content licenses could legally justify permanent storage, though no explicit confirmation exists for private calls.
Distinction matters: temporary caching presents minimal risk if secured and promptly deleted. Permanent storage creates ongoing exposure, especially given security vulnerabilities and third-party sharing.
When and Why Recording Might Occur (Legitimate Scenarios)
Legal compliance: Court orders or law enforcement requests. Policy confirms data sharing for compliance, potentially including call recordings when legally required.
Content moderation: 24/7 moderation and face verification suggest active monitoring for violations. User reports of inappropriate behavior would require recorded evidence—necessitating continuous recording or user-initiated recording during reports.
Service improvement: Platforms may record sample calls for quality assessment, algorithm training, technical issue identification. Broad content licenses could legally permit this, though undisclosed for private calls.
Identifying Recording Indicators in Chamet App
Professional platforms display clear cues when recording: red dots, banner notifications, audio announcements, status changes. Presence/absence reveals platform transparency priorities.
Chamet's interface lacks obvious recording indicators during private calls. This could mean recording doesn't occur OR the platform chooses not to notify. Notification permission enables alerts, but no recording started notifications appear.
9 embedded trackers monitor behaviors, though specific functions regarding calls remain undisclosed. Trackers could log call events without user-visible indicators.
Visual Cues That Signal Active Recording
Standard indicators: red recording dots, This call is being recorded banners, status bar changes, icon modifications. Professional platforms implement these for consent law compliance requiring all parties know when recording occurs.
Chamet shows participant feeds, call duration, standard controls (mute, camera toggle, end call) but lacks dedicated recording status indicators. Absence doesn't prove non-recording—just means users aren't explicitly notified.
Check device native indicators: iOS shows orange dots (microphone active), green dots (camera active); Android similar. System-level indicators confirm app hardware access but don't distinguish live transmission from recording/storage.
Notification Systems and User Alerts
Notification system delivers: new messages, incoming calls, verification codes, promotions. No documented notification type alerts users to call recording initiation/completion—significant transparency limitation.
Two-factor authentication demonstrates Chamet can deliver time-sensitive, action-specific notifications when desired. Absence of recording notifications appears deliberate, not technical limitation.
Privacy settings allow opting out of marketing but offer no control for call recording notifications. Asymmetry suggests recording (if occurring) is treated as core service function, not optional feature.
Hidden Indicators Most Users Miss
Subtle indicators experienced users monitor:
Unexpected battery drain during/after calls (background processing)
Unusual data usage patterns (upload beyond live transmission)
App behavior changes after calls (delayed responses suggesting background tasks)
Device storage fluctuations (temporary file creation)
344 strings/secrets in code include configuration parameters and data handling instructions. Security researchers analyzing code can identify behaviors not disclosed in user documentation.
Network monitoring tools detect transmission patterns. Data upload continuing post-call suggests processing that could include uploading recorded content. Requires technical expertise beyond typical users.
Complete Privacy Settings Audit for Chamet Users
Privacy controls reside in account settings (profile menu). Available: disable stranger messages, control location sharing, manage notifications, opt-out of marketing. Lacks granular controls for call recording, retention periods, third-party sharing preferences.
Users can request data access, correction, deletion through account settings. Policy doesn't specify response timeframes, data completeness guarantees, or whether certain categories (like call recordings) are exempt.
Verification requirements—SMS (2-3 minutes), face verification (24-48 hours)—create additional collection points users must accept for full features. Face verification for hosts is mandatory, requiring biometric data submission.
Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing Privacy Controls

Open Chamet, tap profile icon
Select Settings
Locate Privacy Settings or Privacy & Security
Review toggles for stranger messages, location, profile visibility
Access Account Settings for data management
Find Data & Privacy to request access/deletion
Check notification settings for alert control
Interface provides basic controls but lacks advanced options. No toggles for prevent call recording, limit retention, or restrict third-party sharing beyond marketing opt-out.
Essential Settings to Enable for Maximum Protection
Configure immediately:
Disable stranger messages: Prevents unsolicited contact, reduces scammer exposure
Turn off location sharing: Prevents geographic data sharing/storage
Limit profile visibility: Restricts who views your information
Disable promotional notifications: Reduces marketing partner data sharing
Enable two-factor authentication: Adds account security layer
Review third-party services: Disconnect unnecessary integrations
Device-level protections: restrict Chamet's contact access, limit background data, disable mic/camera when not using app, regularly review permissions.
Advanced Privacy Features Most Users Overlook
Data access request: Underutilized but forces Chamet to disclose collected information, revealing practices not obvious from normal usage. Takes weeks but provides valuable transparency.
Account deletion: Most comprehensive action. Policy doesn't specify whether deletion triggers immediate removal or eventual deletion. Some platforms retain deleted data for months/years.
Device-level permission limits: Revoke location when not needed, disable background refresh, restrict photo library to selected photos only. These supplement in-app settings.
Data Retention and Storage Duration Breakdown
Policy confirms global processing adhering to laws but provides no specific retention timelines. Transparent platforms specify: call metadata retained 90 days, account data stored for account lifetime plus 1 year. Absence suggests indefinite retention or undisclosed periods.
Different data types follow different schedules. Account info persists for account lifetime plus retention period. Transaction data faces longer retention (financial regulations). Communication metadata might be retained for improvement/compliance. Content (if recorded) could face longest retention or immediate deletion.
Data sharing with affiliates, service providers, third parties complicates retention. Even if Chamet deletes data, shared data might persist in third-party systems under different policies.
How Long Call Metadata Remains on Servers
Call metadata (duration, participants, timestamps, quality metrics) serves legitimate purposes: billing verification, quality analysis, abuse prevention. Industry standards: 90 days to 2 years. Chamet provides no specific timeline.
Database interactions (SQL queries in code) confirm persistent database storage. Whether databases include call metadata and duration remains undisclosed. 8 non-parameterized SQL queries represent vulnerabilities exposing stored metadata to unauthorized access.
Assume indefinite storage absent explicit limits. Conservative assumption protects privacy by encouraging behavior appropriate for permanent records.
Regional Differences in Data Retention Policies
Requirements vary dramatically. EU GDPR requires data minimization and specified retention with automatic deletion. US regulations vary by state/data type. Asian jurisdictions range from strict localization to minimal restrictions.
Global processing means different users' data stored in different jurisdictions under different frameworks. German user might have EU server data subject to GDPR; other regions different protections. Policy doesn't specify how location affects handling.
Jurisdictional complexity creates uncertainty about applicable rights. GDPR grants EU users strong access/deletion rights; other regions fewer protections. Policy states users can request access/deletion but doesn't clarify equal application regardless of location.
Your Rights to Request Data Deletion
Policy explicitly states users can request deletion through account settings. Critical details unspecified: response timeframes, verification requirements, deletion scope (all vs. specific categories), exceptions (legal compliance retention), confirmation procedures.
Submitting deletion request:
Access account settings
Locate data management/privacy section
Select Request Data Deletion
Confirm identity through verification
Specify deletion scope if options provided
Await confirmation (timeframe unspecified)
Document requests with screenshots/timestamps. If no response within 30-60 days, users in certain jurisdictions can file complaints with data protection authorities.
Encryption and Security Measures Protecting Your Calls
Chamet claims end-to-end encryption—only participants should decrypt content, servers unable to access unencrypted data. But 38 weak crypto algorithms in version 3.1.1 raise serious questions about implementation quality. Weak algorithms vulnerable to attacks breaking encryption.
End-to-end encryption requires proper implementation: key generation, exchange, algorithms, secure storage. Vulnerabilities in any component compromise the system. 164 total vulnerabilities (61 medium-severity) suggest implementation gaps affecting encryption effectiveness.
32 possible secrets in code represent another concern. Hardcoded secrets (encryption keys, API credentials, tokens) can be extracted by attackers. Professional practices require secure storage outside code—their presence is a red flag.
Current Encryption Standards Used by Chamet
Specific algorithms/protocols remain undisclosed. Industry-standard end-to-end encryption uses Signal Protocol, WebRTC with DTLS-SRTP, or similar implementing authenticated encryption with forward secrecy. Forward secrecy ensures compromised keys don't expose past communications.
38 weak crypto algorithms suggest outdated/insufficient methods for some functions: deprecated MD5/SHA-1 for hashing, DES/3DES for encryption, insufficient key lengths. Whether these impact call encryption specifically remains unclear.
Encryption protects data during transmission but doesn't prevent endpoint recording (participant devices) or guarantee post-transmission deletion. Even with perfect encryption, participants can screen-record, and servers might store encrypted data indefinitely.
End-to-End Encryption: What's Actually Implemented
True end-to-end encryption means keys exist only on participant devices—servers can't access keys or decrypt content. Prevents server-side recording of decrypted content, though servers might store encrypted data/metadata. Distinction between encrypted in transit (decrypted on servers) and end-to-end (only participants decrypt) is critical.
Claim should mean private calls can't be recorded in decrypted form on servers. But lack of technical documentation plus identified vulnerabilities prevents independent verification. Transparent platforms publish security whitepapers or undergo third-party audits.
9 trackers could collect metadata even if content encrypted. Trackers monitor behavior, engagement, feature usage—doesn't require breaking encryption but reveals privacy-relevant communication patterns.
Server Security Protocols and Infrastructure Protection
Server security layers: network security (firewalls, intrusion detection), access controls (authentication, authorization), data protection (encryption at rest, secure deletion), monitoring (audit logs, anomaly detection). 6.7/10 security rating suggests moderate implementation with improvement room.
16 task hijacking vulnerabilities indicate process/data flow management weaknesses. Could allow malicious apps to intercept Chamet data or manipulate behavior. Even with strong server security, client-side vulnerabilities compromise privacy before data reaches servers.
Infrastructure protection includes physical server security, employee access controls, incident response. Global processing means servers in multiple locations with potentially different standards. Users lack visibility, requiring trust without independent verification.
Common Privacy Misconceptions Debunked
Privacy discussions involve misconceptions overstating or understating risks. 67.6% negative review rate involving privacy breaches indicates widespread concerns, though not all breaches necessarily involve recording policies.
Misconception: End-to-end encryption guarantees complete privacy. Reality: Encryption protects content during transmission but doesn't prevent endpoint recording, metadata collection, or vulnerabilities compromising encryption. Critical tool but not complete solution.
Misconception: Absence of recording indicators proves non-recording. Reality: Platforms can record without indicators, relying on policy disclosures as legal notification. Lack of indicators doesn't confirm or deny recording.
Myth vs Reality: What Chamet Actually Records
Myth: End-to-end encryption means Chamet can't access any data. Reality: Encryption (if properly implemented) protects call content but doesn't prevent metadata collection (duration, participants, timestamps), account info, device IDs, IP addresses, other data in policy. Extensive collection beyond call content.
Myth: Recording would show an indicator. Reality: Indicators are transparency features, not legal requirements everywhere. Platforms can record if policies disclose practices. Lack of indicators doesn't prove non-recording.
Myth: Deleting account immediately removes all data. Reality: Policy doesn't specify deletion timeframes or whether certain categories retained for compliance/business. Assume eventual deletion, not immediate removal.
Myth: Private calls are completely private. Reality: Policy confirms sharing with affiliates, service providers, third parties. Legal compliance may mandate authority disclosure. Vulnerabilities could enable unauthorized access. Private describes intended audience, not guaranteed confidentiality.
Understanding User Consent and Recording Permissions
Consent occurs through accepting terms/privacy policy during account creation. Blanket consent grants broad permissions for data collection/use as described. Users not reading policies unknowingly consent to extensive collection.
Content license users grant permits using content for service operation. Broad language could theoretically justify recording if deemed necessary, though not explicitly stated. Vague language creates legal permission for undisclosed practices.
Meaningful consent requires informed understanding. Policy length/complexity plus requirement to accept creates framework favoring platforms. Read policies carefully and assume anything not explicitly prohibited might occur.
Third-Party Access: Separating Facts from Fear
Policy explicitly states sharing with affiliates, service providers, third parties for delivery, improvement, compliance. Confirmed third-party access differs from unauthorized breach access. Both represent risks through different mechanisms.
Legitimate access includes: cloud hosting (storing data), analytics (processing usage), payment processors (handling transactions), content delivery networks (optimizing media). Each operates under own policies/standards, creating complex handling web beyond Chamet's control.
Unauthorized access could occur through 164 vulnerabilities, particularly 61 medium-severity issues and 16 task hijacking vulnerabilities. Security gaps enable malicious actors to intercept data, access storage, manipulate behavior—independent of official sharing.
Expert Tips for Protecting Your Privacy on Chamet
Privacy protection requires multi-layered approach: in-app settings, device controls, behavioral practices, realistic risk assessment. No single action provides complete protection; combining strategies significantly reduces exposure. Balance privacy with functionality—maximum privacy often limits features.
6 risky permissions (camera, mic, location, photo library, notification, others) create multiple collection points. Each granted permission increases exposure. Regularly audit and revoke non-essential permissions. Location isn't necessary for video calls—disable without affecting core features.
Privacy protection is ongoing, not one-time configuration. Apps update regularly, potentially changing settings or introducing new collection. Policies change, sometimes expanding collection/sharing. Regular audits ensure continued protection.
Pre-Call Privacy Checklist (7 Essential Steps)
Before initiating/accepting private calls:
Verify app permissions: Check device settings; revoke location, contacts, photo library if not needed
Review privacy settings: Confirm stranger messages disabled, location off, profile visibility restricted
Check device recording status: Ensure no screen/call recording apps running
Assess environment: Verify surroundings don't expose sensitive info in video feed
Consider content sensitivity: Evaluate if conversation appropriate for platform with unclear policies/vulnerabilities
Verify participant identity: Confirm calling intended person; impersonation/compromise could expose communication
Prepare alternative: Have more secure platform available for highly sensitive conversations
These steps reduce but can't eliminate risks given policy ambiguities and vulnerabilities.
Behavioral Best Practices for Sensitive Conversations
For sensitive information:
Avoid identifying information: Don't disclose full names, addresses, financial details enabling identity theft/harassment if exposed
Use vague references: General references provide context without detailed records
Assume recording: Behave as if recorded and could be disclosed publicly
Limit duration: Shorter calls create smaller footprints, reduce vulnerability exposure
Verify before sharing: Explicitly confirm other party's identity and private setting
Use alternative platforms for critical content: Reserve Chamet for casual conversations; use clearer-policy platforms for sensitive discussions
Behavioral practices complement technical protections, creating defense-in-depth.
Red Flags That Indicate Privacy Risks
Warning signs suggesting elevated risks:
Unexpected app behavior: Crashes, freezes, unusual performance could indicate malware/compromise
Unusual data usage: Higher consumption than expected suggests background transmission
Battery drain: Excessive consumption indicates background processing possibly including upload
Unsolicited contact: Messages/calls from strangers despite privacy settings suggest settings malfunction
Account access notifications: Alerts about unfamiliar login attempts indicate potential compromise
Privacy policy changes: Update notifications should trigger immediate review for new collection/sharing
When encountering red flags: review settings, change passwords, revoke permissions, consider whether continued use appropriate.
Your Legal Rights and Data Access Options
Legal rights vary dramatically by jurisdiction—some robust, others minimal. Understanding applicable rights enables exercising protections and informed decisions. Policy's adhering to applicable laws means different users have different rights based on location.
EU users benefit from GDPR: access personal data, correct inaccuracies, request deletion (right to be forgotten), restrict processing, data portability, object to certain activities. Applies to any platform processing EU residents' data regardless of platform location. California residents have similar CCPA/CPRA rights with some scope/enforcement differences.
Jurisdictions without comprehensive laws have fewer guaranteed rights but can still request access/deletion per Chamet's policy. Platform's commitment to honor requests without legal obligation depends on practices and advocacy. Document requests and follow up persistently.
GDPR and Regional Privacy Law Compliance
GDPR compliance requires: lawful processing basis, data minimization, purpose limitation, storage limitation, integrity/confidentiality, accountability. Chamet's policy addresses some requirements but lacks specificity on storage duration and processing purposes for different categories.
Broad content licenses and vague retention potentially conflict with GDPR's minimization and storage limitation. EU users can file complaints with national data protection authorities, which investigate and impose penalties. Provides practical leverage.
Other regions: research local laws. Brazil's LGPD, Canada's PIPEDA, Australia's Privacy Act, various frameworks provide different protections. Even without comprehensive laws, sector-specific regulations (financial, health, children's data) may apply.
How to Request Your Personal Data from Chamet
Data access request (Subject Access Request/SAR) forces platforms to disclose collected data. Provides transparency into practices, enables verifying accuracy/completeness.
Access account settings
Navigate to privacy/data management
Look for Request My Data, Download My Data
Submit request, note date
Await response (GDPR: 30 days; other jurisdictions vary or none)
Review provided data for completeness/accuracy
Follow up if delayed/incomplete
Data should include all personal information: account details, profile, contacts, communication metadata, transactions, potentially call records if existing. Gaps could indicate data not collected or incomplete compliance.
Filing Complaints and Escalation Procedures
When Chamet doesn't respond or users suspect violations, formal complaints provide escalation:
EU users: File with national data protection authorities (DPAs). Each member state has DPA investigating GDPR violations, imposing penalties. Typically file online through DPA websites.
California users: File with California Attorney General's office enforcing CPRA. AG investigates violations, imposes penalties.
Other jurisdictions: Research local privacy enforcement agencies. Many have data protection/consumer protection agencies handling privacy complaints.
When filing, provide:
Detailed violation description
Documentation of direct resolution attempts (screenshots, correspondence)
Specific law provisions allegedly violated
Impact on privacy
Desired resolution
Regulatory complaints take months but provide leverage individuals lack.
Maximizing Your Chamet Experience with BitTopup
While navigating privacy complexities, users still seek social features and premium functionality. Accessing premium requires purchasing Chamet diamonds. Selecting secure, reliable recharge protects financial privacy, ensures successful transactions without unnecessary payment exposure.
BitTopup provides trusted Chamet diamond recharges with privacy/security advantages: competitive pricing maximizing value, fast delivery ensuring quick crediting for immediate access, secure transaction processing protecting payment info through industry-standard encryption.
Privacy-conscious users should extend concerns to payment transactions. Using reputable third-party platforms like BitTopup separates payment from social platform, reducing exposure. Established reputation and high ratings provide confidence in security and customer service.
Secure Payment Methods for Privacy-Conscious Users
BitTopup supports multiple payment methods for privacy-aligned options:
Credit/debit cards: Convenient but create detailed records linked to identity
Digital wallets: Separation layer between source and merchant, reducing exposure
Cryptocurrency: Highest privacy for crypto-comfortable users, requires technical knowledge
Prepaid cards: Enable anonymous purchases if obtained without identity verification
Selecting through established platforms like BitTopup rather than unknown third parties reduces fraud risk, ensures customer support for transaction issues.
Premium Features That Enhance Privacy Protection
Premium features (via diamond purchases): enhanced profile customization, priority customer support, various social features. Premium doesn't explicitly include privacy enhancements, but priority support assists with privacy-related issues faster than standard channels.
Users investing in premium should ensure privacy settings properly configured. Premium accounts may attract more attention, making settings like disabling stranger messages and limiting visibility even more important.
Exclusive BitTopup Benefits for Chamet Users
BitTopup advantages:
Competitive pricing: Regular promotions, competitive rates maximize diamond value
Fast delivery: Automated processing credits diamonds within minutes
Secure transactions: Industry-standard payment security protects financial info
Wide payment options: Multiple methods accommodate preferences
Excellent customer service: Responsive support assists with questions, resolves issues
High user ratings: Established reputation, positive reviews provide confidence
Transaction privacy: Third-party recharge separates payment data from social platform
For privacy-conscious users seeking premium features while minimizing exposure, BitTopup provides reliable, secure recharge complementing privacy-protective practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Chamet automatically record private video calls?
Chamet's policy doesn't explicitly state whether private 1-on-1 calls are recorded/stored. Claims end-to-end encryption (should prevent server access to content), but absence of clear non-recording statement, plus broad content licenses and user content collection, creates uncertainty. Assume calls could be recorded given lack of explicit confirmation otherwise.
How long does Chamet store call data on servers?
Policy provides no specific retention timeline for call data, metadata, or user information. States global processing adhering to laws but doesn't specify storage durations. Absent disclosed limits, assume indefinite storage. Policy confirms users can request deletion through account settings, though response timeframes and completeness unspecified.
Can other users record my Chamet video calls without permission?
Yes. Other users can record using device screen recording (iOS/Android built-in, third-party apps) regardless of Chamet policies. Chamet can't prevent participants recording on own devices. Assume any call could be recorded by other participant; avoid sharing sensitive information problematic if recorded/shared.
What privacy settings should I enable on Chamet for maximum protection?
Enable: disable stranger messages (prevents unsolicited contact), turn off location sharing (prevents geographic exposure), restrict profile visibility (limits who views info), disable promotional notifications (reduces marketing sharing), enable two-factor authentication (account security). Device-level: revoke unnecessary permissions (location, contacts, photo library), limit background data, regularly audit settings.
Does Chamet use end-to-end encryption for private calls?
Chamet claims end-to-end encryption but technical details aren't publicly documented. Security analysis identified 38 weak crypto algorithms, raising questions about quality/effectiveness. True end-to-end should prevent servers accessing decrypted content, but vulnerabilities and lack of transparency prevent independent verification. Treat claims cautiously given vulnerabilities and absence of third-party audits.
How can I request deletion of my Chamet call history?
Access account settings, navigate to privacy/data management, look for data deletion options. Policy confirms users can request access, correction, deletion through settings, though procedures, timeframes, scope aren't detailed. Submit requests, document with screenshots/timestamps. If no response within 30-60 days, users in jurisdictions with privacy laws (EU, California) can file complaints with data protection authorities to enforce deletion rights.
Protect your privacy while enjoying premium Chamet features! Top up Chamet coins securely through BitTopup - trusted platform offering instant delivery, competitive rates, complete transaction privacy. Visit BitTopup now for exclusive Chamet recharge deals!

